
Closest to Jupiter (inward of the Galilean moons) are the four small moons:
 |
 ) is the innermost of Jupiter's known satellites:
) is the innermost of Jupiter's known satellites:
orbit: 128,000 km from Jupiter
diameter: 40 km
mass: 9.56e16 kg
Metis was a Titaness who was the first wife of Zeus (Jupiter).
Discovered by Synnott in 1979 (Voyager 1).
Metis and Adrastea lie within Jupiter's main ring. They may be the source of the material comprising the ring.
Small satellites within a planet's rings are sometimes called "mooms".
 |
orbit: 129,000 km from Jupiter
diameter: 20 km (23 x 20 x 15)
mass: 1.91e16 kg
Adrastea, the distributor of rewards and punishments, was the daughter of Jupiter and Ananke.
Discovered by graduate student David Jewitt (working under Danielson) in 1979 (Voyager 1).
Metis and Adrastea orbit inside the synchronous orbit radius and inside the Roche limit. They may be small enough to avoid tidal disruption but their orbits will eventually decay.
Adrastea is one of the smallest moons in the solar system.
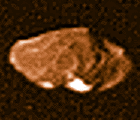 |
orbit: 181,300 km from Jupiter
diameter: 189 km (270 x 166 x 150)
mass: 7.17e18 kg
Amalthea was the nymph who nursed the infant Jupiter with goat's milk.
Discovered by Barnard 1892 September 9 using the 36 inch (91 cm) refractor at Lick Observatory. Amalthea was the last moon to be discovered by direct visual observation (as opposed to photography).
 Amalthea and Himalia are Jupiter's
fifth and sixth largest moons;
they are about the same size but only
1/15 the size of next larger one, Europa.
Amalthea and Himalia are Jupiter's
fifth and sixth largest moons;
they are about the same size but only
1/15 the size of next larger one, Europa.
Like most of Jupiter's moons, Amalthea rotates synchronously; its long axis is pointed toward Jupiter.
Amalthea is the reddest object in the solar system. The reddish color is apparently due to sulfur originating from Io.
 Its size and irregular shape imply that Amalthea is a fairly
strong, rigid body. Its composition is probably more like an
asteroid's than like the Galilean moons.
Its size and irregular shape imply that Amalthea is a fairly
strong, rigid body. Its composition is probably more like an
asteroid's than like the Galilean moons.
Like Io, Amalthea radiates more heat than it
receives from the Sun (probably due to the electrical currents
induced by Jupiter's magnetic field).
 |
orbit: 222,000 km from Jupiter
diameter: 100 km (100 x 90)
mass: 7.77e17 kg
 Thebe was a nymph, daughter of the river god Asopus.
Thebe was a nymph, daughter of the river god Asopus.
Discovered by Synnott in 1979 (Voyager 1).
The image above shows Thebe's leading side which has three or four large (compared to Thebe's size) craters. The image at left shows the trailing side.